Chapter:01 Basic Components of PLC or DCS Control System.
There are five basic components in a PLC system:
Power Supply (PSU-Power Supply Unit)
Input Section/Input modules
PLC DCS Processor or CPU
Output Section/Output modules
Memory (User Memory and IO Memory)
What is Processor or CPU in PLC?:
This central processing unit (CPU) of PLC, that is a microprocessor by design and functionality.
The main function of this unit is to sense input values via its I/O modules, generate control signals following the input signals and the predefined instruction (stored in the memory unit as program).
Stores the control program and data in its memory
Reads the status of connected input devices, Executes the control program, Commands connected outputs to change state based on program execution
For example: Turn a light on, start a fan, adjust a speed, or temperature
A CPU interface Let’s look at each in more detail.

What are Input/Output Modules in PLC?
Physically connect to field devices
Input modules convert electrical signals coming in from input field devices such as pushbuttons, to electrical signals that the PLC can understand.
Output modules take information coming from the PLC and convert it to electrical signals the output field devices can understand, such as a motor starter, or a hydraulic solenoid valve.
What are Input Modules in PLC?
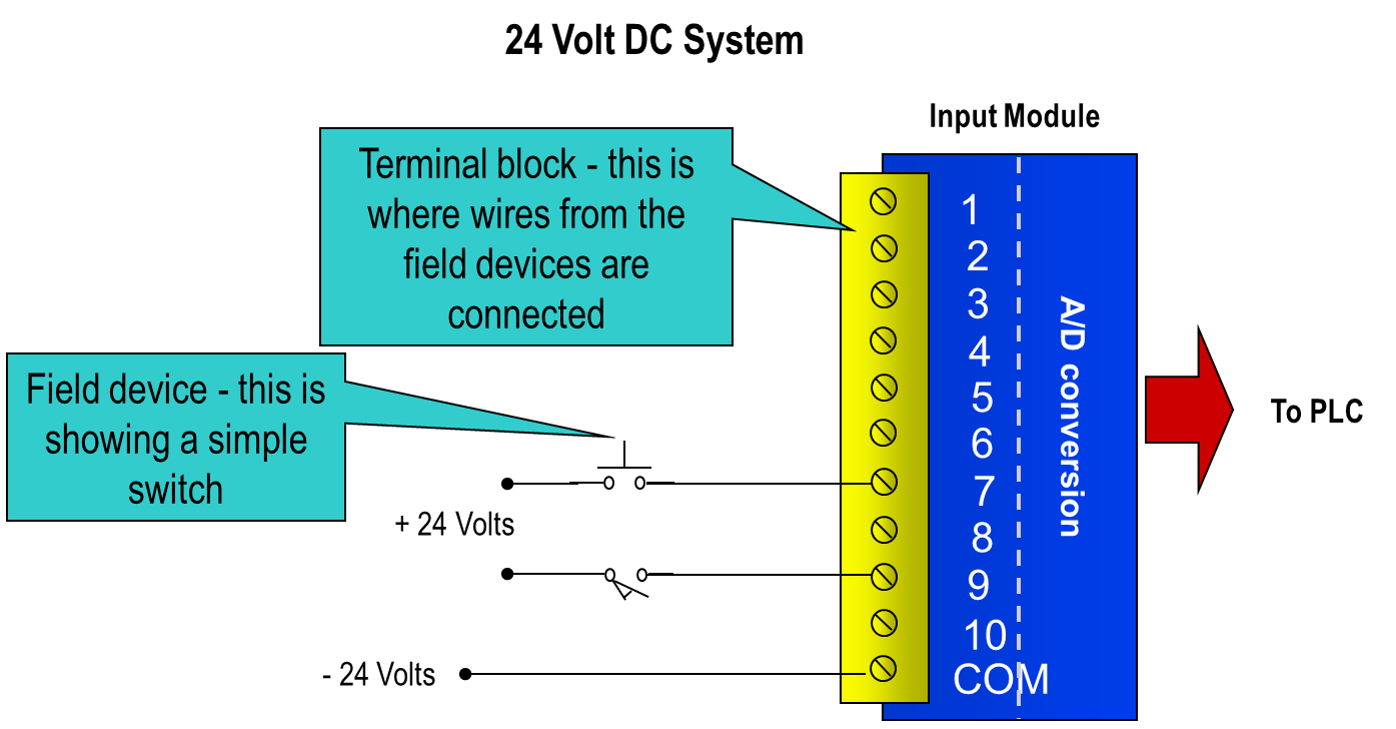
Input modules interface directly to devices such as switches and temperature sensors.
Input modules convert many different types of electrical signals such as 120VAC, 24VDC, or 4-20mA, to signals which the controller can understand.
Input modules convert real world voltage and currents to signals the PLC can understand. Since there are different types of input devices, there is a wide variety of input modules available, including both digital and analog modules.
What is Difference between Discrete and Analog Module?
Discrete modules use only a single bit to represent the state of the device. For example, a switch is either open or closed. Therefore, the bit is either a 0 (switch is open) or a 1 (switch is closed). Discrete modules are also known as Digital modules.
Analog modules use words to represent the state of a device. An analog signal represents a value.. For example, the temperature could be 5, 9, 20, 100, etc degrees. Analog modules use a value, such as 52, rather than a 0 or 1 to represent the state of the device.
What are Discrete Modules in PLC?
Devices that are either on or off, such as a pushbutton, get wired to discrete modules. Discrete modules come in a variety of types, such as 24VDC or 120VAC. You can buy discrete modules that allow you to typically connect anywhere from 2 to 32 devices, with the most popular being 16 devices.
Since it takes only 1 bit to represent the state of a device, a 16 point discrete module only requires 16 bits of memory in the controller to store the states of all the points on the module.
What are Analog Modules in PLC?
Devices that have a number associated with them, such as a temperature sensor, get wired to analog modules. Analog modules come in a variety of types, such as 4 to 20 mA or 0 to 10 VDC. You can buy analog modules that allow you to connect anywhere from 2 to 16 devices.
Since it takes 1 word to represent a number, a 16 point analog module requires 16 words of memory in the controller to store the value of all the numbers on the module. Each word in a PLC takes 16 or 32 bits (depending on the PLC), therefore it takes 16 or 32 times the amount of PLC memory to store analog points vs. digital points.
What are Output Modules in PLC?
Output modules interface directly to devices such as motor starters and lights
Output modules take digital signals from the PLC and convert them to electrical signals such as 24VDC and 4 mA that field devices can understand.
Output modules take a signal from a PLC and convert it to a signal that a field device needs to operate. Since there are different types of output devices, there is a wide variety of output cards available, including both digital and analog cards.
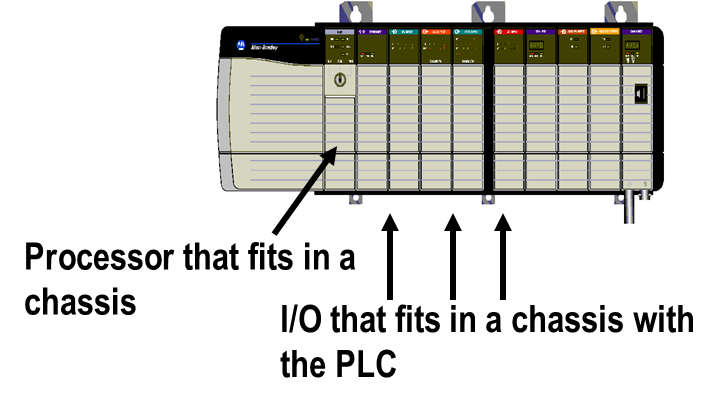
What is Chassis/Backplane in PLC/DCS?
All PLCs need some method of communicating between the controller, I/O and communications modules. Here are three ways used to accomplish this communications between the various components that make up the PLC system.
Modules are installed in the same chassis as the PLC and communicate over the chassis backplane
Modules are designed to “plug” into each other. The interconnecting plugs form a backplane. There is no chassis
Modules are built into the PLC. The modules come together in one physical block. The backplane in this case is transparent to the user.
Below is an example of a backplane in a chassis based system. You can see the backplane in the area where the modules are not inserted. The modules have connectors that plug into the black connectors on the backplane. All of the connectors on the backplane are connected together electrically.
What is Power Supply in PLC?
A power supply is needed to provide power to the PLC and any other modules. Power supplies come in various forms:
Power supply modules that fit into one of the slots in a chassis
External power supplies that mount to the outside of a chassis
Stand alone power supplies that connect to the PLC or I/O through a power cable
Embedded power supplies that come as part of the PLC block.
