Section-4:Compute/Math Instructions
Use this instruction:
- ADD
- SUB
- MUL
- DIV
- MOD
- SQR
- NEQ
- ABS
If you want to
- add two values
- subtract two values
- multiply two values
- divide two values
- determine the remainder after one value is divided by another
- calculate the square root of a value
- take the opposite sign of a value
- take the absolute value of a value
You can mix data types, but loss of accuracy and rounding error might occur and the instruction takes more time to execute. Check the S:V bit to see whether the result was truncated.
The bold data types indicate optimal data types. An instruction executes faster and requires less memory if all the operands of the instruction use the same optimal data type, typically DINT or REAL.
A compute/math instruction executes once each time the instruction is scanned as long as the rung-condition-in is true. If you want the expression evaluated only once, use any one-shot instruction to trigger the instruction.
Add (ADD)
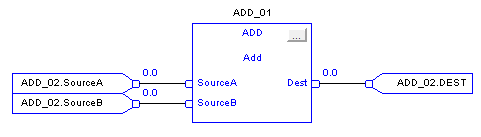
When enabled, the ADD instruction and the operator ‘+’ adds Source A to Source B.
Subtract (SUB)
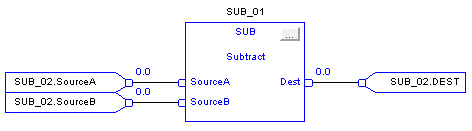
When enabled, the SUB instruction and the operator ‘-‘ subtracts Source B from Source A.
Multiply (MUL)
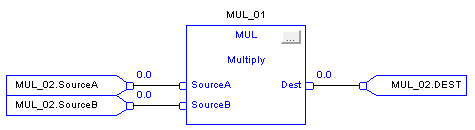
When enabled, the MUL instruction and the operator ‘*’ multiplies Source A with Source B.
Divide (DIV)
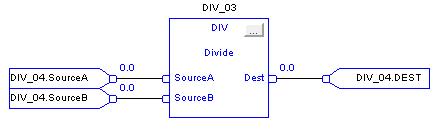
When enabled, the DIV instruction and the operator ‘/’ divides Source A by Source B.
Modulo (MOD)
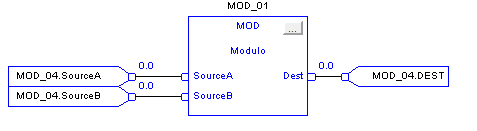
When enabled, the MOD instruction and the operator divides Source A by Source B and places the remainder in Dest. This is done using the algorithm:
Dest = Source A – (truncate ( Source A / Source B) * Source B)
Square Root (SQR)
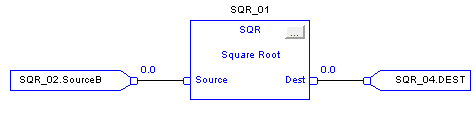
The SQR instruction and operator computes the square root of the Source and places the result in Dest.
Negate (NEG)
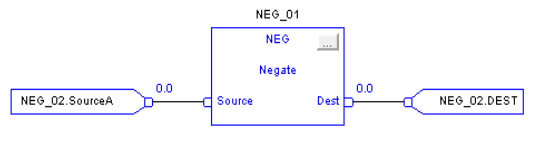
When enabled, the NEG instruction and operator subtract the Source value from zero.
Absolute Value (ABS)
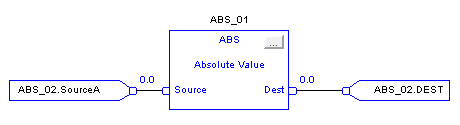
When enabled, the ABS instruction and operator take the absolute value of Source. The instruction stores the result in Dest while the operator simply returns the result. An overflow is indicated if the result is the maximum negative integer value, e.g. -128 for SINT, -32,768 for INT and -2,147,483,648 for DINT.
